Mailwatch
About
Xfce4 Mailwatch Plugin is a multi-protocol, multi-mailbox mail watcher for the Xfce4 panel.
Features
- IMAP and Secure IMAP support
- POP3 and Secure POP3 support
- Local Mbox mailbox support
- Local Maildir mailbox support
- Local MH-Maildir mailbox support
- GMail support
- Fully multithreaded design: no panel lockups
- Informative new-message breakdown in tooltip
- Ability to run program on new messages or button click
- Informative logger to help track down mail connection problems
Usage
The Mailwatch icon remains grey (default color) as long as it does not detect any new mail. As soon as it checks, and there is new mail, the mail icon will turn gold (default color). By clicking on the mail icon, a command, which can be defined in the properties dialog box, will be launched. A mail check can be forced by middle-clicking the Mailwatch icon in the panel. Right-clicking on the Mailwatch icon shows a context menu from which you can choose Properties to access the configuration options. There are also menu items for forcing an update and the about box.
Properties
Xfce4 Mailwatch Plugin has a variety of configuration options. Access to the configuration is gained by right-clicking the panel icon, and by choosing Properties.
Mailwatch main settings:
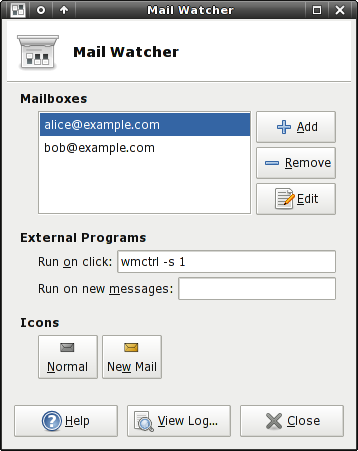
Mailboxes
The main controls for managing mailboxes are Add, Edit, and Remove. At later stage, we'll walk through adding and configuring each mailbox type.
External Programs
Mailwatch can launch your mail user agent (or any other program) when the panel icon is clicked. The name of the executable together with possible startup parameters goes in the Run on click entry field. You can also define the command to be executed when Mailwatch detects new mail by typing the desired command in the Run on new messages entry field. Note that the command is executed once for each time Mailwatch detects new mail, regardless of the number of new messages received.
Icons
The icons that Mailwatch displays in the panel are configurable. Both the Normal and New Mail buttons present a file chooser dialog, which you can use to select your preferred icons.
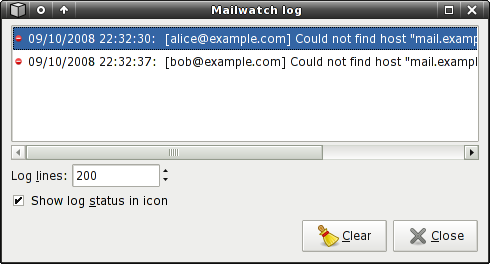
Logging
Mailwatch includes a logging mechanism as well. It provides information about errors and other noteworthy events that take place. The log is accessible via the View Log button. There's also a setting to Show log status in icon in the log dialog which, if enabled, provides a visual indication of new log events in the panel.
Log Window:
Panel Indicator:
Mailbox configuration
In this section we walk through adding and configuring each type of mailbox.
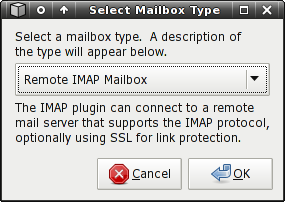
To add a new mailbox, click Add in the main configuration dialog and a mailbox type selection dialog will appear. The dialog presents each supported mailbox type in the dropdown list, as well as an informative description of the mailbox in the label below.
Mailbox type selection:
IMAP
IMAP, acronym for Internet Message Access Protocol, is a quite common mailbox format. An IMAP mailbox is a remote mailbox, so it requires various configuration options to be able to contact the remote IMAP server and get information on the mailbox.
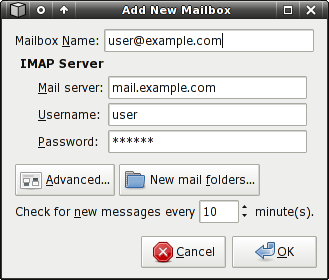
To create an IMAP account in Mailwatch, choose Remote IMAP Mailbox in the mailbox type chooser dialog, and you will be presented with the IMAP settings dialog.
IMAP Settings Dialog:
Mailbox Name
A descriptive name for the mailbox. The name entered here will appear on the Mailwatch icon tooltip, which indicates mailboxes that have new mail. This setting is required, regardless of the mailbox type.
MAP Server
- Mail server - The hostname of the remote mail server.
- Username - The username to use while accessing the mailbox.
- Password - The password to use.
Interval
Defines how often Mailwatch accesses the mailbox to see if there's new mail. You shouldn't set this too low, as it will create unnecessary network traffic. It's not recommended to set this lower than 5 minutes, unless you're really sure your service provider is okay with that.
The default setup uses unencrypted connections and the default IMAP folder. It is highly recommended that you select an encrypted connection type if your mail provider supports it. Others may require an encrypted connection. For that there's the advanced settings dialog.
Advanced Settings
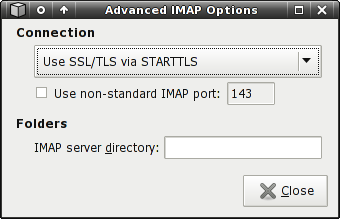
Advanced IMAP settings:
Connection
If your IMAP service provider supports encryption for client connections, you should take advantage of it. There are generally two implementations of encrypted connections. The most common one uses port 993 for client connections and encrypts the connection from the start. The other, less common method, uses the ordinary IMAP port for initializing the connection and then, before any sensitive data is transmitted, initializes the encryption with the STARTTLS command. Mailwatch provides default settings for these setups, which are Use SSL/TLS on alternate port and Use SSL/TLS via STARTTLS respectively. If you're not sure which option your mail provider supports, you can test via trial and error by using each setting, and then checking the log viewer for errors.
There's also the possibility of using a non-standard IMAP port, if your service provider so requires. Just check the box, and type in the appropriate port. The box will pre-fill the default port for the selected connection type.
Folders
In addition of the connection related settings, you can set the directory on the server where your mail is stored using the IMAP server directory text box. This setting may not be necessary on some systems. If you see a large number of strange folder names when looking in the New mail folders dialog box, you may need to set this, often to something like “mail”, “Mail”, or “Maildir”.
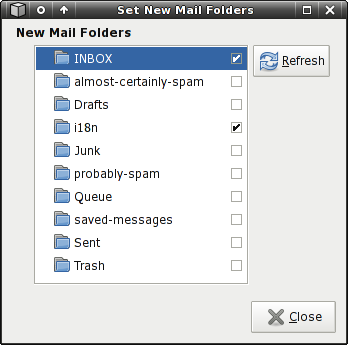
New mail folders:
Since IMAP supports viewing mail in multiple folders, it's possible that you'd receive new mail in folders other than your inbox. If that's the case, you can use the New Mail Folders dialog to instruct Mailwatch to check mail in multiple folders. The dialog will connect to your mail server and fetch a list of folders for you to select. Of course, you'll need to enter the server information first.
POP3
POP3, short for Post Office Protocol Version 3, is another common type of remote mailbox. Because of its remote nature, the settings for POP3 are almost the same as IMAP, with some omissions, as POP3 isn't as advanced a protocol as IMAP.
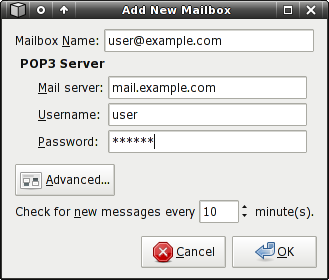
POP3 Settings:
Mailbox Name
A descriptive name for the mailbox. The name entered here will appear on the Mailwatch icon tooltip, which indicates mailboxes that have new mail. This setting is required, regardless of the mailbox type.
POP3 Server
- Mail server - Hostname of the POP3 server.
- Username - Username to authenticate with.
- Password - Password to use in authentication.
Interval
Defines how often Mailwatch accesses the mailbox to see if there's new mail. You shouldn't set this too low, as it will create unnecessary network traffic. It's not recommended to set this lower than 5 minutes, unless you're really sure your service provider is okay with that.
While for most users providing these settings should be enough, there are also advanced settings for those who need additional features.
Advanced Settings
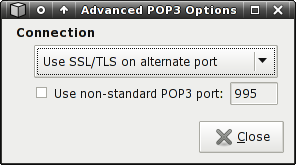
POP3 Advanced Settings:
Connection
If your POP3 service provider supports encryption for client connections, you should take advantage of it. There are generally two implementations of encrypted connections. The most common one uses port 995 for client connections and encrypts the connection from the start. The other, less common method, uses the ordinary POP3 port for initializing the connection and then, before any sensitive data is transmitted, initializes the encryption with the STLS command. Mailwatch provides default settings for these setups, which are Use SSL/TLS on alternate port and Use SSL/TLS via STARTTLS respectively. If you're not sure which option your mail provider supports, you can test via trial and error by using each setting, and then checking the log viewer for errors.
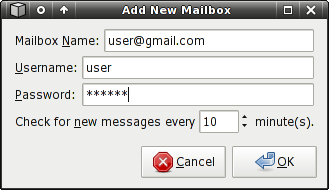
GMail
Mailwatch can also watch your GMail mailbox. Mailwatch does this securely by using HTTPS and GMail's RSS feed.
GMail Settings:
GMail Server
- Username - Your GMail username.
- Password - Your GMail password.
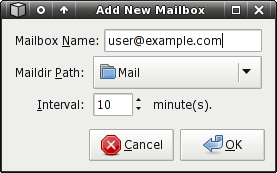
Maildir
Maildir is a mailbox format for local mailboxes and thus there is no
hostname, etc. to configure, but merely a directory where your mail is
stored. A Maildir mailbox has a certain distinguishable hierarchy,
which defines the mailbox (and which Mailwatch expects to find). A
Maildir consists of a top level directory (~/.maildir for example),
which contains three subdirectories (cur, new, tmp).
Maildir Settings:
Mailbox Name
A descriptive name for the mailbox. The name entered here will appear on the Mailwatch icon tooltip, which indicates mailboxes that have new mail. This setting is required, regardless of the mailbox type.
Maildir Path
The toplevel directory of your Maildir. (Note: This is the main mail folder, not any of the three subdirectories.)
Interval
Defines how often Mailwatch checks the mailbox for new mail. It is safe to set a value as low as 1 minute, as this is presumably on a local filesystem, or at least a local network.
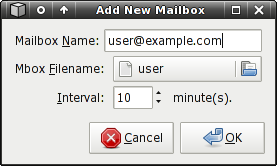
Mbox
Mbox is another very common local mailbox format in which each folder is a single, large file that contains all your messages. Because of this, Mbox expects to find a specially-formatted Mbox file instead of a directory tree.
Mbox Settings:
Mailbox Name
A descriptive name for the mailbox. The name entered here will appear on the Mailwatch icon tooltip, which indicates mailboxes that have new mail. This setting is required, regardless of the mailbox type.
Mbox Filename
The location of your Mbox file (often /var/mail/$USER).
Interval
Defines how often Mailwatch checks the mailbox for new mail. It is safe to set a value as low as 1 minute, as this is presumably on a local filesystem, or at least a local network.
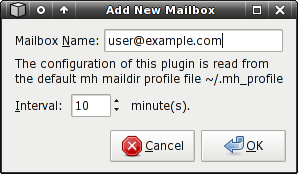
MH Maildir
MH Maildir is a variant of the Maildir format. For a MH Maildir
mailbox, Mailwatch reads your $HOME/.mh_profile file for its
configuration, so there are no actual settings specific to MH
mailboxes.
MH Maildir Settings:
Mailbox Name
A descriptive name for the mailbox. The name entered here will appear on the Mailwatch icon tooltip, which indicates mailboxes that have new mail. This setting is required, regardless of the mailbox type.
Interval
Defines how often Mailwatch checks the mailbox for new mail. It is safe to set a value as low as 1 minute, as this is presumably on a local filesystem, or at least a local network.
Downloads
The normal (and best) way to get this plugin is to use the package manager or port system of your operating system.
If it isn't available there, or if you want a different version, you can download it in source form from http://archive.xfce.org/src/panel-plugins/xfce4-mailwatch-plugin.
You can retrieve the current development version of the plugin from Xfce’s Git repository using the following command:
git clone git://git.xfce.org/panel-plugins/xfce4-mailwatch-plugin
It can also be browsed at http://git.xfce.org/panel-plugins/xfce4-mailwatch-plugin.
Requirements
- Xfce 4 base libraries, version 4.8.0 or greater
- Xfce 4 Panel, version 4.8.0 or greater
- Optional but recommended: GNU TLS, version 1.2.0 or greater and libgcrypt, version 1.2.0 or greater, for secure IMAP and POP3 support
Installation
In order to install a released version fo Mailwatch, issue the following commands from the root of the Mailwatch source tree:
$ ./configure --prefix=${xfce_prefix}
$ make
$ make install
Where ${xfce_prefix} is the location where Xfce 4 is installed. On
most systems this should be /usr. The make install portion should
be run as root (or via sudo) if the prefix is a system location.
In order to install the Git version of Mailwatch, issue the following commands instead:
$ ./autogen.sh --prefix=${xfce_prefix}
$ make
$ make install
Contributions
Bug reports and patches can be submitted on Xfce Bugzilla. Development discussion should take place on the Xfce Goodies Development Mailing List. The Mailwatch plugin is easily extensible to support extra mailbox types if needed.
If you’d like to see Mailwatch translated into another language, please visit the page with informations for translators.